What’s New: Dubai has enacted the Housing Dispute Settlement Law (Law No. 8 of 2025) effective January 1, 2026, establishing specialized dispute resolution mechanisms with 20-day mediation timelines and 30-day adjudication periods. The Dubai Land Department’s Amicable Settlement Centre has expanded its digital services, while the Rental Disputes Settlement Centre now processes cases through remote litigation systems. Recent amendments to RERA regulations provide protection for off-plan property buyers following developer delays. Common questions we receive involve navigating the complex dispute resolution pathways and understanding when court intervention becomes necessary versus alternative resolution methods.
Author Credentials: This guide is prepared by Abdulla Alateibi Advocates certified real estate dispute specialists with extensive experience in Dubai property litigation and alternative dispute resolution. Our team maintains active practice before the Rental Disputes Settlement Centre, Dubai Courts, and the Dubai Land Department’s Amicable Settlement Centre, bringing practical insights from successfully resolving hundreds of property disputes across residential, commercial, and off-plan developments throughout Dubai.
Scope of Legal Advice: This article provides general information about Dubai real estate dispute resolution within Abdulla Alateibi Advocates’ expertise in UAE property law and litigation. For specific advice regarding your property dispute circumstances, consultation with qualified legal counsel familiar with your particular situation and property type is recommended.
Dubai’s real estate market, while offering tremendous opportunities for property owners and investors, also presents various challenges that can lead to disputes. Understanding real estate disputes property owners commonly face is essential for protecting investments and ensuring timely resolution. With recent legislative enhancements including the Housing Dispute Settlement Law and expanded alternative dispute resolution mechanisms, property owners now have multiple pathways for addressing conflicts efficiently and cost-effectively.
Common Types of Real Estate Disputes in Dubai
Real estate disputes in Dubai encompass a wide range of conflicts arising from property transactions, development projects, rental agreements, and ownership issues. Understanding these common dispute types helps property owners recognize potential issues early and take appropriate action.
Developer-Related Disputes
Off-plan property disputes represent one of the most frequent categories of real estate disputes in Dubai’s market:
- Delayed Handover and Completion: Developers failing to deliver properties within agreed timelines create significant challenges for buyers who have made substantial financial commitments. Dubai Law No. 13 of 2008 regulates escrow accounts and provides protection, but delays remain common requiring legal intervention to enforce completion or obtain compensation.
- Quality and Specification Issues: Disputes arise when delivered properties fail to meet promised specifications, approved plans, or quality standards shown in marketing materials. Buyers discovering material deviations have legal recourse through Dubai Land Department complaint procedures and court action for damages or specific performance.
- Payment and Refund Disputes: Conflicts over payment schedules, disputed amounts, and refund entitlements when projects are cancelled or significantly delayed require careful review of Sale and Purchase Agreements and escrow account status. Recent regulations provide buyer protection for refund claims.
Rental Agreement Conflicts
Landlord-tenant disputes form another major category handled by specialized forums:
- Unlawful Rent Increases: RERA’s rental index establishes permitted increase limits based on market comparisons, yet landlords sometimes attempt excessive hikes exceeding statutory caps. Tenants can challenge these through Rental Disputes Settlement Centre proceedings with RERA calculator evidence.
- Eviction and Termination Disputes: Conflicts over notice periods, eviction grounds, and lease termination procedures require careful application of Dubai Law No. 26 of 2007. Landlords must provide proper notice (12 months for personal use/sale, 30 days for breach) and follow prescribed procedures to avoid unlawful eviction claims.
- Security Deposit Disputes: Disagreements over deposit deductions, return timelines, and condition assessments at tenancy end create frequent conflicts. Landlords bear burden of proving damage beyond normal wear and tear, with photographic evidence and professional assessments required.
- Maintenance and Repair Obligations: Disputes over responsibility for maintenance, repairs, and property upkeep involve application of statutory landlord obligations under tenancy law. Landlords must maintain properties in habitable condition and repair defects affecting tenant use.
Based on our experience with Dubai clients, rental disputes represent a significant portion of property-related conflicts we handle, with security deposit and eviction issues being most prevalent. Proper documentation and early legal consultation significantly improve resolution outcomes.
Quick Reference: Dispute Resolution Forums
| Forum | Best For | Timeline | Filing Fee | Appeal Rights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amicable Settlement Centre | Negotiable disputes, developer-buyer conflicts | Days to weeks | Free | N/A (voluntary) |
| RDSC | All landlord-tenant disputes | 45-60 days | 3.5% of annual rent (min AED 500, max AED 20,000) | 30 days to Appeal Court |
| Dubai Courts | Complex legal issues, title disputes | 6-12 months | 7.5% of claim value (max AED 30,000) | 30 days to Appeal Court |
| DIAC Arbitration | Commercial disputes, international parties | 6-9 months | Variable by claim value | Limited review rights |
Actionable Takeaway: Document all property conditions, communications, and agreements thoroughly from transaction inception to create strong evidence supporting your position in potential disputes.
Developer Disputes and Off-Plan Property Issues
Off-plan property purchases create unique dispute scenarios requiring specialized legal knowledge and strategic approaches. The relationship between developers and buyers involves complex contractual obligations, escrow regulations, and regulatory oversight.
Construction Delays and Non-Delivery
Delayed project completion represents the most common developer dispute:
- Permissible Delays vs. Breach: Dubai regulations distinguish between force majeure delays and developer breach. Force majeure includes government approvals and unforeseen circumstances. Contracts typically include extension clauses. However, prolonged unexplained delays constitute breach justifying buyer remedies. These include contract cancellation, refunds, and damages.
- Escrow Account Protection: Dubai Law No. 13 of 2008 mandates escrow account maintenance for off-plan projects. Payments release upon construction milestone completion. Buyers can request escrow account statements from Dubai Land Department and challenge unauthorized releases or non-payment situations.
Legal Remedies Available: Buyers facing developer delays can pursue multiple remedies:
- Filing complaints with Dubai Land Department’s Real Estate Regulatory Agency
- Initiating court proceedings for specific performance or damages
- Claiming against developer performance bonds
- Seeking refunds with interest and compensation
Quality and Specification Defects
Disputes over delivered property quality require careful documentation:
- Material Deviations from Plans: When completed properties differ substantially from approved plans, buyers can file complaints with Dubai Municipality and Dubai Land Department. Material deviations affecting property value or usability justify damages claims or price reduction demands.
- Construction Defects and Deficiencies: Latent defects discovered post-handover remain developer responsibility during warranty periods. Structural issues, MEP (mechanical, electrical, plumbing) defects, and finishing problems require professional assessment reports supporting compensation or rectification claims.
- Snagging and Handover Disputes: Pre-handover inspections identifying defects (snagging) create obligations for developer rectification before final handover. Developers sometimes pressure buyers to accept properties with outstanding defects, creating disputes over completion status and payment release.
Financial Disputes with Developers
Payment and refund conflicts require understanding escrow regulations and contractual terms:
- Payment Schedule Disputes: Disagreements over payment milestone achievement, calculation methods, and timing create conflicts. Buyers should verify milestone completion independently before releasing payments. Challenge premature payment demands not aligned with actual construction progress.
- Refund Claims and Calculations: When projects are cancelled or buyers exercise cancellation rights, disputes arise over refund amounts, interest entitlements, and deduction clauses. Dubai regulations protect buyer deposits in escrow accounts, but contract terms affect final refund calculations.
- Interest and Penalty Claims: Buyers may claim interest on delayed refunds and penalties for developer breach. Developers sometimes counterclaim for buyer payment delays. Contract penalty clauses must comply with UAE law limiting excessive penalties subject to court reduction.
Developer Dispute Resolution Flowchart
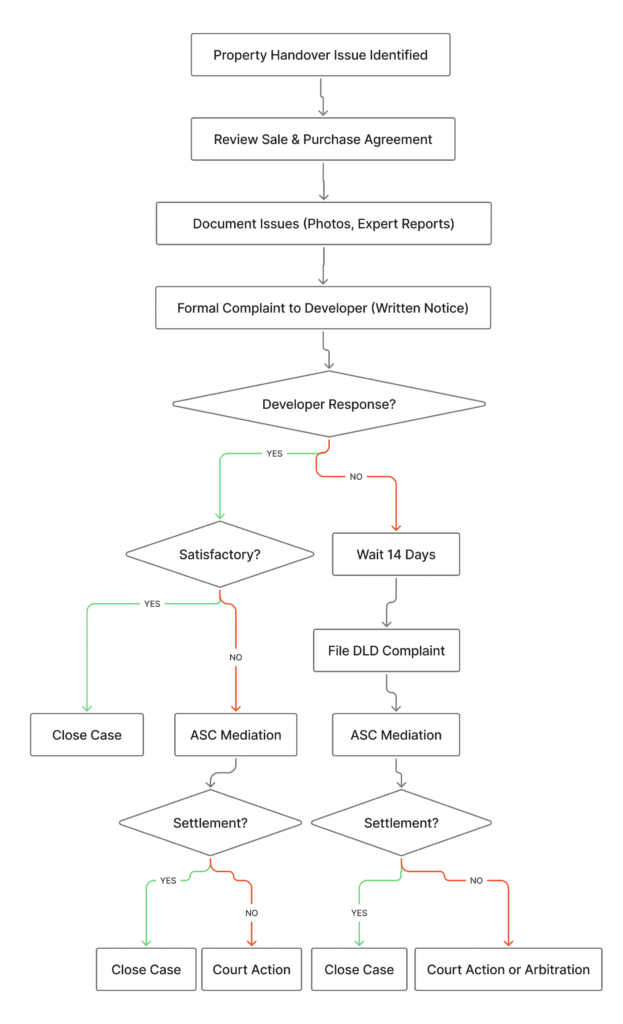
In our experience with Dubai clients, developer disputes often involve multiple interconnected issues. These require a legal strategy addressing contractual, regulatory, and practical resolution approaches simultaneously.
Actionable Takeaway: Engage qualified surveyors and legal counsel before final handover to document all defects and preserve legal remedies for quality issues and incomplete work.
Landlord-Tenant Rental Disputes
Rental real estate disputes between landlords and tenants involve specific procedures and specialized forums established by Dubai Law No. 26 of 2007 and subsequent amendments.
Rent Increase and Payment Disputes
Rental payment conflicts require understanding RERA regulations and tenancy law:
RERA Rental Index Compliance: Dubai’s rental increase caps are determined by RERA’s rental calculator comparing current rent to market rates:
| Current Rent vs. Market Rate | Permitted Increase |
|---|---|
| Within 10% of market rate | 0% (no increase allowed) |
| 11-20% below market rate | Up to 5% |
| 21-30% below market rate | Up to 10% |
| 31-40% below market rate | Up to 15% |
| More than 40% below market | Up to 20% (maximum) |
Landlords exceeding these limits face dispute challenges at RDSC.
- Payment Default and Grace Periods: When tenants default on rent payments, landlords must follow prescribed notice procedures before pursuing eviction. A 30-day notice providing opportunity to cure default is required before court proceedings. Tenants can dispute payment amounts, calculation methods, or claim payments made.
- Utility and Service Charge Disputes: Conflicts over utility bill responsibilities, DEWA (Dubai Electricity and Water Authority) charges, and service charge obligations require contract interpretation. Landlords cannot disconnect utilities as enforcement mechanism. Such actions constitute violations subject to penalties.
Eviction and Lease Termination Conflicts
Eviction disputes involve strict procedural requirements:
Lawful Eviction Grounds: Dubai Law No. 26 of 2007 establishes specific eviction grounds:
30-Day Notice Required:
- Non-payment of rent (after grace period)
- Property misuse or illegal activities
- Subletting without landlord permission
- Breach of tenancy contract terms
12-Month Notice Required:
- Landlord personal use (must occupy for minimum 1 year)
- Property sale to third party
- Major renovation or demolition requiring evacuation
Notice Requirements and Procedures: All eviction notices must be notarized and properly served through registered channels. 12-month notices for personal use/sale require landlord declarations verified by Dubai Land Department. Improper notice procedures invalidate eviction attempts.
Tenant Defenses and Challenges: Tenants can challenge eviction grounds, notice adequacy, landlord’s genuine intention for personal use, and compliance with procedural requirements. Sham evictions (false personal use claims followed by re-renting) subject landlords to penalties and tenant compensation.
Property Condition and Maintenance Disputes
Responsibility for property upkeep creates frequent conflicts:
Landlord Maintenance Obligations: Landlords must:
- Maintain properties in habitable condition
- Repair structural defects
- Ensure functioning utilities and MEP systems
- Address defects affecting tenant use
- Perform maintenance obligations specified in tenancy contracts
Failure to perform required maintenance justifies tenant remedies including rent reduction, repair cost recovery, or lease termination.
Tenant Damage Claims: Landlords claiming tenant-caused damage must prove:
- Damage occurred during tenancy
- Damage exceeds normal wear and tear
- Damage results from tenant negligence or misuse
Professional assessments, photographic evidence comparing move-in and move-out conditions, and repair cost estimates support damage claims.
Security Deposit Deduction Disputes: Security deposit conflicts arise when landlords make excessive or unjustified deductions. Tenants can challenge deductions through Rental Disputes Settlement Centre, requiring landlords to prove legitimate damage and reasonable repair costs. Courts often reduce excessive claims.
RDSC Filing Process Timeline
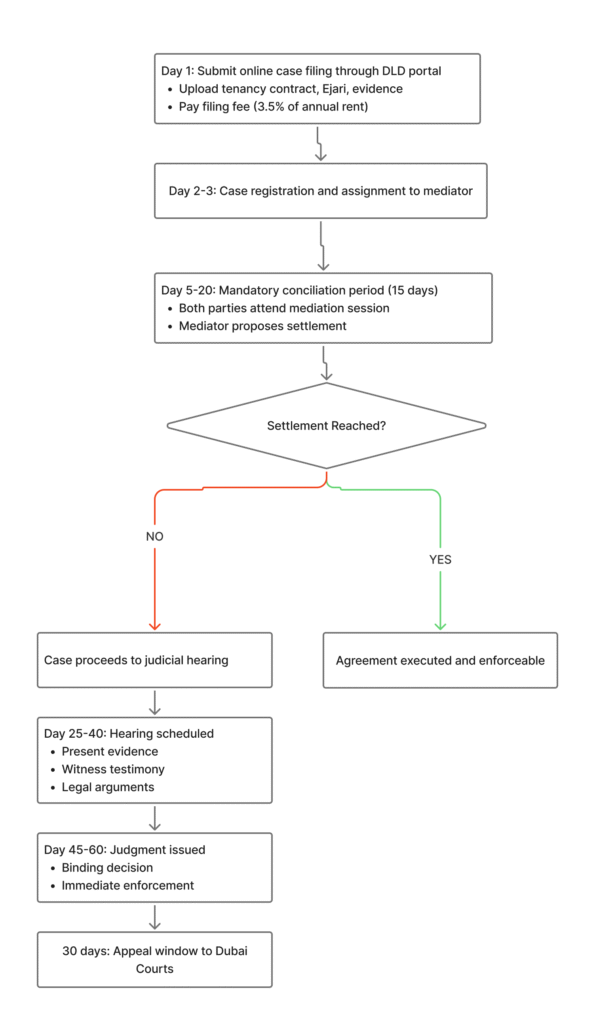
Our experience with regulatory changes shows that Rental Disputes Settlement Centre proceedings typically resolve within 45-60 days including conciliation and judgment phases. This makes this forum significantly faster than general civil courts.
Actionable Takeaway: Conduct thorough property inspections with photographic documentation at tenancy commencement and termination to establish clear baseline for condition disputes.
Property Ownership and Title Disputes
Title and ownership real estate disputes involve complex legal issues requiring thorough investigation and often lengthy resolution processes.
Fraudulent Transactions and Title Defects
Ownership legitimacy disputes raise serious legal concerns:
Fraudulent Property Transfers: Cases involving forged documents, unauthorized signatures, or identity fraud require immediate action:
- Court injunctions preventing further transfers
- Police reports documenting fraud
- Dubai Land Department notifications
Federal Law No. 5 of 1985 and local DLD regulations provide correction procedures for fraudulent entries.
- Boundary and Survey Disputes: Conflicts over property boundaries, encroachments, and survey inaccuracies require official survey reports from Dubai Municipality. Property owners discovering boundary discrepancies can request official surveys and pursue court action for boundary determination or encroachment removal.
- Multiple Ownership Claims: Competing ownership claims arising from successive sales, inheritance disputes, or registration errors require title investigation and court determination. Dubai Land Department records provide presumptive evidence but can be challenged with superior proof.
Co-Ownership and Joint Property Disputes
Shared ownership creates unique conflict potential:
Co-Owner Rights and Obligations: Joint owners hold undivided interests with rights to use, occupy, and enjoy the property. Disputes arise over:
- Exclusive possession attempts
- Rental income distribution
- Expense sharing
- Improvement decisions requiring majority consent or court resolution
Partition and Sale Disputes: Co-owners seeking property division can request partition through court proceedings when voluntary agreement fails. Courts may order physical division (if feasible) or partition by sale with proceeds distributed according to ownership shares.
Management and Decision-Making Conflicts: Joint ownership decisions regarding property management, renovation, leasing terms, and sale require consensus or majority approval. Deadlocked situations may require court-appointed managers or compulsory sale orders.
Inheritance and Family Property Disputes
Property succession creates complex legal issues:
- Succession Rights Under UAE Law: Islamic succession principles govern Muslim property owners (unless testamentary planning exists). Non-Muslims can elect home country law application through registered wills. Disputes arise over succession share calculations, estate distribution, and competing claims.
- Will Execution and Estate Disputes: Challenges to will validity, interpretation conflicts, and estate administration disputes require Dubai Courts jurisdiction. Property transfers require succession certificates or will probate establishing rightful heirs before Dubai Land Department processes ownership transfers.
- Family Agreement Enforcement: Property distribution agreements among heirs require proper documentation and registration to be enforceable. Informal family arrangements often create later disputes requiring court intervention for equitable distribution or property sale.
Based on our experience with Dubai clients, title disputes often involve multiple interconnected legal issues. These include criminal fraud investigations, civil ownership claims, and administrative correction procedures requiring coordinated legal strategy.
Actionable Takeaway: Conduct title due diligence through licensed lawyers before property purchase including ownership verification, encumbrance searches, and court proceeding checks to prevent title dispute involvement.
Construction and Contract Disputes
Construction-related real estate disputes involve contractors, developers, engineers, and property owners in complex contractual relationships governed by standard form contracts and UAE construction law principles.
Contractor Performance Disputes
Construction contract breaches create significant conflicts:
Defective Workmanship Claims: Property owners discovering construction defects can claim damages for:
- Rectification costs
- Diminished property value
- Consequential losses
Professional engineer assessments quantifying defects and repair costs support claims against contractors and design professionals.
Delay and Liquidated Damages: Construction contracts typically include liquidated damages clauses for delayed completion. Contractors facing delay claims often counterclaim for owner-caused delays:
- Design changes
- Payment delays
- Site access issues
They seek extension of time relief from penalties.
Payment and Milestone Disputes: Conflicts over payment milestone achievement, work valuation, variation orders, and final accounts require detailed contract interpretation. Quantity surveyor assessments provide objective analysis. Contractors claiming payment often face owner counterclaims for defects and incomplete work.
Engineering and Design Disputes
Professional service disputes involve specialized considerations:
Design Defects and Professional Negligence: Property owners suffering losses from defective designs can pursue claims against architects and engineers for professional negligence. Establishing liability requires expert evidence showing design fell below professional standards and caused losses.
Supervision and Certification Disputes: Engineering supervision failures allowing defective construction create liability for supervising engineers. Disputes arise over:
- Inspection adequacy
- Certification accuracy
- Professional obligations under engagement terms
Scope and Fee Disputes: Conflicts over professional service scope, additional services, and fee entitlements require contract interpretation and professional standard application. Engineers claiming unpaid fees often face counterclaims for inadequate services or negligence.
Specialist Construction Issues
Dubai’s construction sector presents unique dispute scenarios:
MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing) Disputes: Complex building systems create specialized disputes over:
- Performance specifications
- Design adequacy
- Installation quality
- Operational efficiency
Expert evidence from MEP engineers supports technical claims.
Contractor Insolvency Issues: When contractors become insolvent mid-project, property owners face:
- Completion costs
- Performance bond claims
- Priority disputes with other contractor creditors
Early legal action preserving rights against bonds and guarantees proves critical.
Multi-Party Construction Disputes: Large projects involving developers, main contractors, subcontractors, designers, and suppliers create complex multi-party disputes. These require careful claim presentation and potential consolidation for efficient resolution.
The Housing Dispute Settlement Law (Law No. 8 of 2025) effective January 2026 establishes specialized mechanisms for Emirati housing construction disputes with 20-day mediation and 30-day adjudication timelines. This reflects Dubai’s commitment to efficient construction dispute resolution.
Actionable Takeaway: Include clear dispute resolution clauses in construction contracts specifying mediation, arbitration, or court jurisdiction to avoid procedural conflicts when disputes arise.
Dispute Resolution Mechanisms and Procedures
Dubai provides multiple real estate disputes resolution pathways, each suited for different dispute types and circumstances. Understanding these mechanisms helps property owners select appropriate forums and procedures.
Amicable Settlement Centre at Dubai Land Department
The ASC represents the most cost-effective dispute resolution option:
ASC Services and Benefits: The Amicable Settlement Centre offers free mediation services for property disputes with experienced mediators having access to DLD databases. Settlements reached are documented and legally binding, providing enforceability without court proceedings. The informal process encourages open communication and creative solutions preserving business relationships.
ASC Procedures:
- Submit dispute details and documentation to ASC (online or in-person)
- ASC mediators facilitate settlement discussions
- Mediators propose solutions based on legal principles and practical considerations
- Draft settlement agreements if parties reach consensus
- Signed agreements become enforceable
- If mediation fails, parties may pursue other remedies
Appropriate Dispute Types: ASC mediation works well for:
- Developer-buyer disputes
- Ownership conflicts
- Service charge disagreements
- Commercial property issues where parties maintain willingness to negotiate
Complex legal questions or parties seeking precedent-setting rulings may require court proceedings.
Rental Disputes Settlement Centre (RDSC)
RDSC provides specialized rental dispute resolution:
RDSC Jurisdiction and Process: All landlord-tenant disputes in Dubai fall under RDSC exclusive jurisdiction. The process includes:
- Mandatory conciliation attempts
- Formal hearings if settlement fails
- Judgments issued within typical timelines
Cases are filed online through DLD portal or service centers with 3.5% of annual rent value filing fees (minimum AED 500, maximum AED 20,000).
RDSC Hearing Procedures: Remote litigation systems enable virtual hearings with digital document submission:
- Conciliation sessions lasting 15 days attempt voluntary settlement
- If unsuccessful, cases proceed to judicial hearing
- Judges evaluate evidence, examine witnesses, and issue binding judgments
- Execution enforcement powers ensure compliance
Appeal Rights: RDSC judgments can be appealed to Dubai Courts Appeal level within 30 days. The appeal process examines legal and procedural correctness rather than re-hearing facts. Second appeals to Cassation Court are limited to legal interpretation issues.
Dubai Courts General Jurisdiction
Complex property disputes often require court intervention:
Court of First Instance Filing: Property disputes exceeding RDSC jurisdiction or requiring complex legal determination are filed with Dubai Courts First Instance level. Filing requires:
- Detailed claim statements
- Supporting documents
- Court fees of 7.5% of claim value (capped at AED 30,000)
Cases typically take 6-12 months for first instance judgment.
Evidence and Expert Reports: Courts may appoint expert committees:
- Surveyors
- Engineers
- Valuers
These assess technical issues, property conditions, or damages. Expert reports significantly influence judgments, making report challenge and rebuttal critical.
Appeal and Cassation Process: First instance judgments can be appealed to Court of Appeal within 30 days presenting legal and factual objections. Cassation Court provides final review limited to legal interpretation and procedural correctness, not factual disputes.
Arbitration for Real Estate Disputes
Alternative dispute resolution through arbitration offers benefits:
Arbitration Advantages: Arbitration provides:
- Confidential proceedings
- Specialized arbitrator expertise in real estate and construction matters
- Faster resolution than court litigation
- International enforceability under New York Convention
Dubai International Arbitration Centre (DIAC) handles numerous property disputes annually.
Arbitration Requirements: Enforceable arbitration requires:
- Written arbitration agreements (in contracts or subsequent arbitration submissions)
- Parties select arbitrators
- Parties determine procedures
- Binding arbitral awards enforceable through courts
Appropriate Arbitration Cases: Arbitration benefits:
- Complex commercial property disputes
- International investor conflicts
- Construction contract disputes
- Parties seeking confidentiality
Simple rental disputes and matters requiring urgent interim relief may suit court proceedings better.
Dispute Resolution Decision Tree
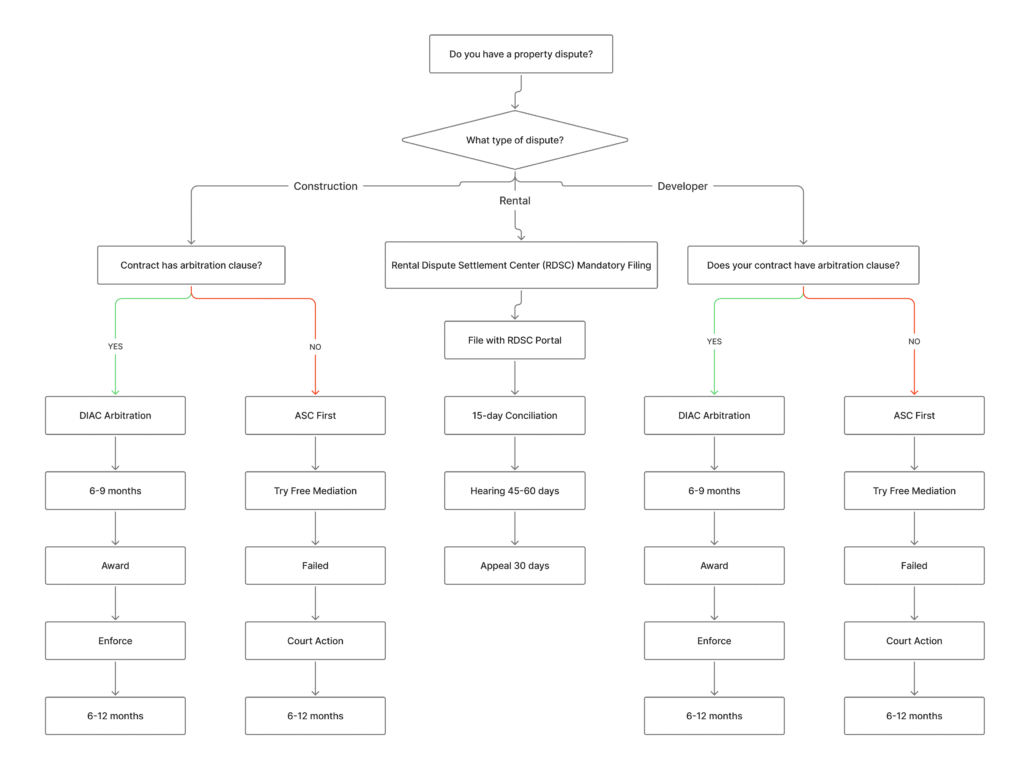
Our experience with regulatory changes demonstrates that selecting appropriate dispute resolution forum significantly impacts timeline, costs, and outcome quality. Early legal consultation helps identify resolution pathways.
Actionable Takeaway: Attempt amicable settlement through ASC or direct negotiation before initiating formal proceedings, as voluntary settlements save time and costs while preserving business relationships.
Legal Remedies and Enforcement Options
Understanding available remedies for real estate disputes helps property owners pursue appropriate relief and enforcement mechanisms ensuring practical resolution.
Monetary Remedies and Compensation
Financial compensation represents primary relief in property disputes:
Damages for Breach of Contract: Property owners proving contract breaches can claim:
- Compensatory damages (direct losses)
- Consequential damages (if reasonably foreseeable)
- Moral damages for reputational harm or emotional distress (in some cases)
UAE law caps penalty clauses deemed excessive, requiring courts to reduce unreasonable amounts.
Specific Financial Claims:
- Rental disputes: Rent payment orders, security deposit returns, utility cost allocations
- Developer disputes: Refund claims with interest calculations, penalty amounts under contract terms, alternative accommodation costs during delays
Valuation and Assessment Issues: Determining appropriate compensation requires:
- Property valuations
- Repair cost estimates
- Market rate assessments
Professional valuers and quantity surveyors provide expert evidence supporting monetary claims and challenging opponent calculations.
Specific Performance and Injunctive Relief
Non-monetary remedies provide critical protection:
Property Transfer Orders: Buyers with valid purchase contracts can seek specific performance orders compelling developers or sellers to:
- Complete property transfers
- Deliver title deeds
UAE courts grant specific performance readily for unique property transactions where monetary damages prove inadequate.
Injunctions Preventing Transfers: Property owners discovering fraudulent transactions or competing claims can obtain urgent injunctions:
- Preventing further property transfers
- Stopping registrations pending dispute resolution
Injunctions preserve status quo protecting legitimate ownership interests.
Mandatory Orders for Rectification: Courts can order developers or contractors to:
- Rectify defects
- Complete unfinished work
- Perform maintenance obligations
Rather than merely awarding monetary compensation. Mandatory orders combined with penalty provisions encourage compliance.
Urgent and Interim Measures
Time-sensitive situations require immediate protection:
Urgent Matters Applications: Dubai Courts urgent matters judge handles applications for immediate temporary relief including:
- Restraining orders preventing property sales
- Injunctions stopping demolition or construction
- Orders preserving disputed properties
- Temporary occupancy determinations pending final resolution
Conditions for Urgent Relief: Applicants must demonstrate:
- Prima facie legal right
- Imminent irreparable harm if relief denied
- Balance of convenience favoring interim protection
Urgent orders remain effective until final dispute resolution, subject to modification if circumstances change.
Enforcement During Proceedings: Parties obtaining favorable urgent orders can enforce immediately through Dubai Courts execution department despite ongoing main case proceedings. Violating urgent orders subjects parties to contempt proceedings and penalties.
Enforcement and Execution Procedures
Obtaining judgments requires effective enforcement:
Execution Through Dubai Courts: Final judgments and arbitral awards are enforced through Dubai Courts execution department. Property-related enforcement includes:
- Compelling property transfers
- Ordering possession delivery
- Authorizing property sales for debt satisfaction
- Implementing specific performance orders
Enforcement Challenges: Judgment debtors may challenge execution applications on procedural grounds or claim judgment satisfaction. Successful enforcement requires:
- Documentation
- Asset identification
- Persistent follow-through overcoming debtor evasion tactics
Cross-Border Enforcement:
- UAE judgment enforcement abroad depends on reciprocal recognition agreements or treaty provisions
- Foreign judgments require UAE court recognition procedures before local enforcement
- Arbitral awards under New York Convention enjoy broader international enforcement
Based on our experience with Dubai clients, enforcement success depends heavily on pre-judgment asset identification and preservation measures preventing judgment-proof situations.
Actionable Takeaway: Consider requesting urgent interim measures early in dispute proceedings to preserve assets, prevent property transfers, and maintain status quo pending final resolution.
FAQ: Your Questions Answered
Common disputes include developer delays and off-plan issues, landlord-tenant rental conflicts, property ownership and title disputes, construction defects, maintenance obligations, security deposit disagreements, and eviction proceedings. Each dispute type has specialized resolution mechanisms through Dubai Land Department, Rental Disputes Settlement Centre, or Dubai Courts depending on the nature and parties involved.
Timeline varies by forum: RDSC rental disputes resolve in 45-60 days typically, ASC mediation takes days to weeks, Dubai Courts first instance proceedings require 6-12 months, and arbitration typically completes within 6-9 months. Complex disputes with appeals or enforcement challenges may extend 18-24 months or longer depending on case complexity and party cooperation.
RDSC is Dubai's specialized forum handling all landlord-tenant disputes with mandatory jurisdiction. Cases are filed online, undergo 15-day conciliation attempts, proceed to judicial hearings if unresolved, and result in binding judgments within typical timelines. Filing fees are 3.5% of annual rent (minimum AED 500, maximum AED 20,000) and remote litigation systems enable virtual proceedings.
: Yes, Dubai Land Department's Amicable Settlement Centre provides free mediationservices for property disputes. Mediation offers informal, confidential proceedings with experienced mediators having DLD database access. Successful mediations result in binding settlement agreements enforceable without court proceedings, saving time and costs while preserving relationships.
First, review your Sale and Purchase Agreement for delay provisions and developer obligations. Request escrow account status from Dubai Land Department verifying payment protections. File complaint with DLD Real Estate Regulatory Agency, attempt amicable settlement through ASC, and consider court proceedings for specific performance, refunds, or damages if delays become unreasonable.
Tenants should verify increase compliance using RERA's rental calculator comparing current rent to market rates. Increases exceeding statutory limits (0-20% based on market differential) can be challenged through RDSC proceedings. File RDSC case with rent increase notice, current contract, RERA calculator results, and evidence of market rates supporting your position.
Landlords must maintain properties in habitable condition, repair structural defects, ensure functioning utilities and MEP systems, address defects affecting tenant use, and perform maintenance obligations specified in tenancy contracts. Failure justifies tenant remedies including repair cost recovery, rent reduction, or lease termination depending on severity.
Gather evidence including photographs documenting conditions, professional assessments from surveyors or engineers, repair cost estimates from contractors, correspondence showing complaints or notices, and comparable property evidence for valuation disputes. Expert reports from qualified professionals significantly strengthen damage claims and valuations.
Law No. 8 of 2025 effective January 2026 establishes specialized mechanisms for Emirati housing construction disputes with structured timelines: 20-day mediation phase (extendable 20 days), 30-day adjudication by judge and specialist committee, and 30-day appeal rights. The law aims to resolve construction disputes quickly preventing delays and protecting family interests.
Yes, RDSC judgments can be appealed to Dubai Courts Appeal level within 30 days examining legal and procedural correctness. First instance court judgments are appealable within 30 days to Court of Appeal. Final appeals to Cassation Court are limited to legal interpretation issues, not factual disputes, with strict procedural requirements.
Essential documents include contracts (sale agreements, tenancy contracts), property documents (title deeds, Ejari registrations), payment records (receipts, bank transfers), correspondence (emails, letters, notices), photographs documenting conditions, and expert reports. Organized documentation significantly improves dispute resolution outcomes and legal position strength.
RDSC filing fees are 3.5% of annual rent value (minimum AED 500, maximum AED 20,000). Dubai Courts charge 7.5% of claim value (capped at AED 30,000). ASC mediation is free. Additional costs include lawyer fees, expert reports, translation services, and enforcement expenses varying by case complexity.
: Rights include escrow account protection under Dubai Law No. 13 of 2008, performance bond claims if applicable, priority claims in developer insolvency proceedings, and potential court action for specific performance or refunds. Act quickly to preserve legal rights, file timely claims, and coordinate with other buyers for collective action if appropriate.
Prevention strategies include thorough due diligence before transactions, written agreements with clear terms, proper Ejari registration for rentals, regular property inspections with documentation, timely communication addressing issues early, and professional legal review before signing contracts. Early legal consultation prevents many disputes and strengthens position when conflicts arise.
Ignoring proceedings results in default judgments against absent parties, loss of legal defenses, enforcement actions including property seizure or transfer orders, additional penalties and costs, and difficulty reversing default judgments. Always respond to legal proceedings through qualified lawyers protecting your rights and presenting defenses appropriately.
Yes, UAE law imposes limitation periods for legal claims. General civil claims have 15-year limitation periods, while specific claims have shorter periods: rental disputes must be filed promptly after dispute arises, developer delay claims should be filed within reasonable time after breach, and fraud claims have specific limitation periods. Consult legal counsel immediately to preserve rights.
Yes, foreign property owners have full access to Dubai's dispute resolution mechanisms regardless of nationality. All property owners, whether UAE nationals, GCC citizens, or other foreign nationals, can file cases with RDSC, Dubai Courts, or pursue arbitration. Legal representation ensures language barriers and procedural requirements are properly managed.
Conclusion
Understanding real estate disputes property owners face in Dubai provides essential foundation for protecting investments and ensuring timely resolution when conflicts arise. From developer delays and rental disagreements to ownership conflicts and construction defects, Dubai’s legal framework offers multiple resolution pathways tailored to different dispute types and circumstances.
The Dubai Land Department’s Amicable Settlement Centre, Rental Disputes Settlement Centre, general court jurisdiction through Dubai Courts, and arbitration options provide dispute resolution mechanisms balancing efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and legal rigor. Recent legislative enhancements including the Housing Dispute Settlement Law demonstrate Dubai’s commitment to continuous improvement of property dispute resolution infrastructure.
Our experience with Dubai clients consistently shows that early legal consultation and proactive dispute management produce significantly better outcomes than reactive approaches after conflicts escalate. Proper documentation, understanding of legal rights and obligations, and strategic selection of appropriate resolution forums prove critical for successful dispute resolution.
As Dubai’s real estate market continues evolving with new developments, regulatory updates, and international investment flows, property dispute complexity increases correspondingly. Professional legal guidance becomes essential rather than optional for navigating this landscape while protecting substantial financial interests.
For property owners facing disputes or seeking preventive advice, we recommend engaging qualified Dubai real estate lawyers early in any conflict. Professional representation ensures rights are protected, appropriate forums selected, and strategies implemented for efficient, cost-effective dispute resolution in Dubai’s property market.
Contact Abdulla Alateibi Advocates for expert guidance on your property dispute →
Legal Disclaimer
This article is provided for general informational purposes only and does not constitute legal advice. The information contained herein reflects general principles of UAE property law and Dubai dispute resolution procedures as of the publication date and should not be relied upon as a substitute for professional legal consultation.
- Abdulla Alateibi Advocates’ Advisory Capacity: This content is prepared by Abdulla Alateibi Advocates within our jurisdictional expertise in Dubai and UAE property law and dispute resolution. Individual dispute circumstances vary significantly, and specific legal advice should always be sought from qualified legal counsel familiar with the particular facts and circumstances of your situation.
- Jurisdictional Scope: This information focuses on Dubai emirate property law and dispute resolution procedures. Other emirates may have varying requirements, and property disputes may involve multiple legal frameworks and jurisdictions depending on property location and parties involved.
- Professional Consultation Recommended: Property disputes involve significant financial interests and legal complexities requiring individual assessment by qualified professionals. We strongly recommend consulting with experienced UAE property dispute lawyers before making any decisions regarding dispute resolution strategies or legal action.
- No Attorney-Client Relationship: Reading this article does not create an attorney-client relationship with Abdulla Alateibi Advocates or any of our affiliated lawyers. For specific legal advice regarding your property dispute circumstances, please contact our office to discuss your particular requirements and establish a formal consultation arrangement.
- Regulatory Currency: Legal requirements, procedural rules, and dispute resolution mechanisms may change. Always verify current requirements with relevant Dubai authorities including Dubai Land Department, Rental Disputes Settlement Centre, and Dubai Courts, and qualified legal counsel before proceeding with dispute resolution decisions.


